Deciphering the Land: A Deep Dive into the Topographical Map of North America
Associated Articles: Deciphering the Land: A Deep Dive into the Topographical Map of North America
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Deciphering the Land: A Deep Dive into the Topographical Map of North America. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Deciphering the Land: A Deep Dive into the Topographical Map of North America
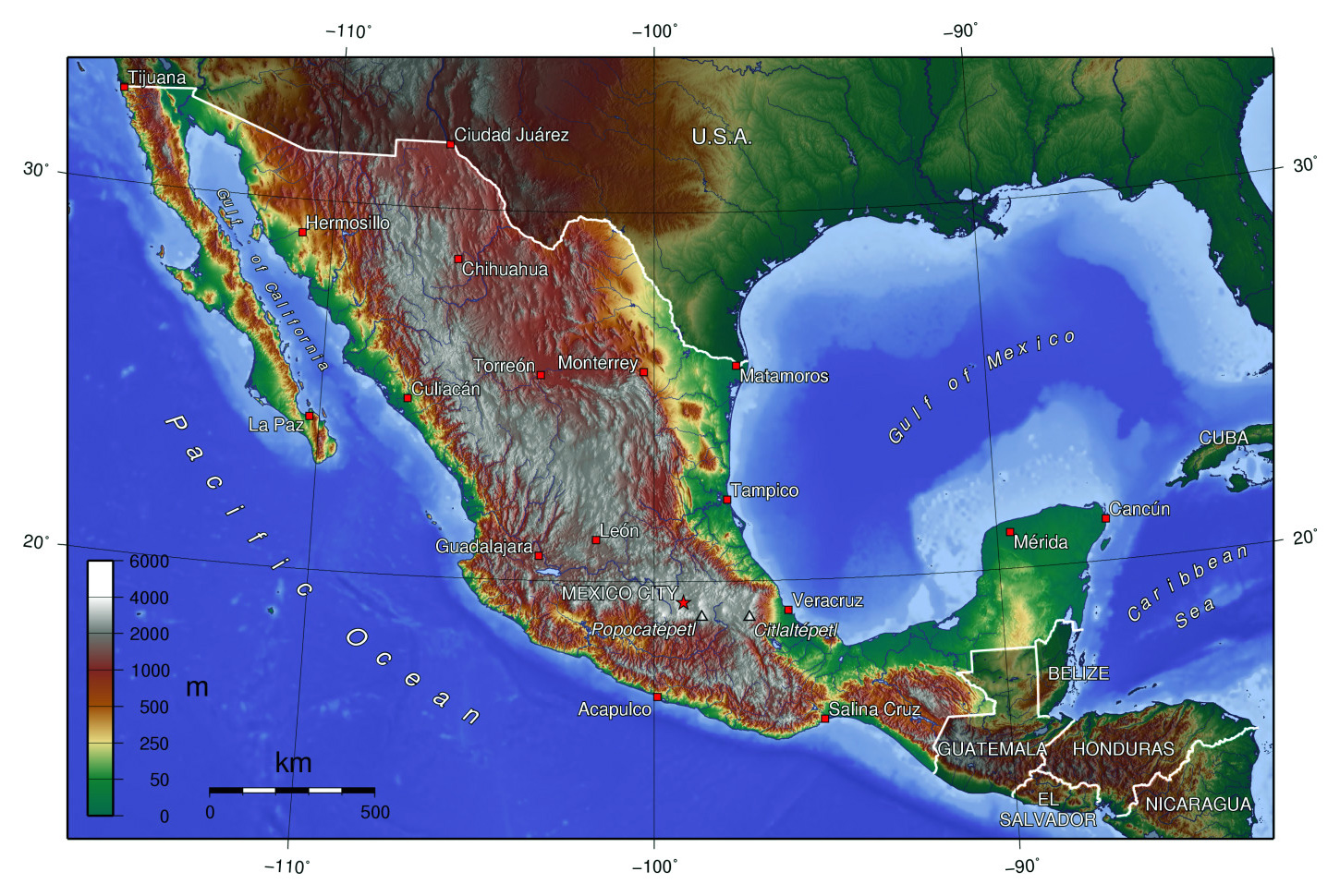
North America, a continent of huge and numerous landscapes, presents a charming problem for cartographers. Representing its intricate topography – from the towering peaks of the Rockies to the sprawling plains of the Midwest, from the deep canyons of the Colorado River to the expansive coastal lowlands – calls for a classy strategy. A topographical map of North America, due to this fact, is way over a easy depiction of landforms; it is a advanced visible narrative of geological historical past, climatic affect, and the ensuing human interplay with the surroundings.
This text will discover the important thing options, interpretations, and purposes of a topographical map of North America, delving into the complexities of its illustration and the insights it presents into the continent’s bodily geography.
The Basis: Contour Strains and Elevation
The cornerstone of any topographical map is the contour line. These traces join factors of equal elevation above a datum, sometimes imply sea degree. The nearer the contour traces are spaced, the steeper the slope. Extensively spaced traces point out a delicate incline or flat terrain. A topographical map of North America makes use of a spread of contour intervals, typically various relying on the dimensions and objective of the map. For example, a large-scale map may make the most of a 10-meter interval to indicate nice element in mountainous areas, whereas a smaller-scale map may make use of a 100-meter and even better interval to characterize the broader reduction of the continent.
Analyzing a North American topographical map reveals instantly the continent’s dramatic reduction. The towering Cordillera, stretching from Alaska to Mexico, is vividly portrayed by intently packed contour traces representing the steep slopes of the Rocky Mountains and the Coast Mountains. Conversely, the huge inside plains of the central United States and Canada are proven by broadly spaced contour traces, reflecting their comparatively flat topography. Main river methods just like the Mississippi, the Missouri, and the Mackenzie are simply recognized by the contour traces following their programs, indicating the valleys they’ve carved via the panorama.
Past Strains: Depicting Extra Options
Whereas contour traces kind the spine of a topographical map, extra options enrich its data density. These embrace:
- Spot Heights: Numerically indicated factors of exact elevation, typically positioned on distinguished peaks or summits. These present essential knowledge for understanding the very best factors inside particular areas.
- Index Contours: Heavier, darker contour traces, often at intervals of a number of normal contour traces (e.g., each fifth contour line). These assist in rapidly figuring out elevation ranges and facilitate map studying.
- Aid Shading: A method that makes use of shading to simulate the impact of sunshine and shadow on the landforms, enhancing the three-dimensional notion of the terrain. That is significantly helpful in visualizing the general topography and figuring out refined variations in slope.
- Hydrography: The illustration of water our bodies, together with rivers, lakes, oceans, and swamps. The route of river movement is usually indicated by arrowheads or hachures.
- Cultural Options: Though primarily targeted on topography, many topographical maps embrace cultural options corresponding to roads, cities, and political boundaries. This context helps to know the connection between human settlement and the bodily surroundings.
Regional Variations: A Various Continent
An in depth examination of a North American topographical map reveals the outstanding range of its landscapes:
- The Cordillera: This huge mountain vary dominates the western fringe of the continent, showcasing the dramatic uplift of the tectonic plates. The map highlights the numerous ranges inside the Cordillera, together with the Rocky Mountains, the Cascade Vary, the Sierra Nevada, and the Coast Mountains, every with its distinctive traits and geological historical past.
- The Inside Plains: Stretching eastward from the Rockies, these plains are characterised by their light slopes and comparatively flat topography. The map reveals the most important river methods that drain this area, together with the Mississippi-Missouri and the Mackenzie River methods, and the huge agricultural potential of those fertile lands.
- The Appalachian Mountains: Situated on the jap seaboard, these older, eroded mountains are depicted with much less dramatic reduction than the Cordillera. The map exhibits the gentler slopes and rounded peaks attribute of those mountains.
- Coastal Plains: Slim coastal plains fringe the Atlantic and Pacific coasts, with various widths relying on the area. The map exhibits the transition from upland to lowland, typically marked by estuaries and deltas.
- Canadian Defend: This historic geological area, overlaying an unlimited space of Canada, is characterised by its rugged, rocky terrain and quite a few lakes. The map reveals the intensive community of lakes and rivers that characterize this area.
Purposes and Interpretations
Topographical maps of North America serve a mess of functions:
- Useful resource Administration: Understanding the topography is essential for managing pure sources, corresponding to forests, minerals, and water. The map aids in figuring out appropriate places for useful resource extraction, infrastructure growth, and conservation efforts.
- City Planning: Topographical knowledge is important for city planning, making certain that infrastructure growth considers the terrain and avoids potential hazards. The map helps in figuring out appropriate places for constructing building, transportation networks, and different city facilities.
- Environmental Research: Topographical maps are important instruments for environmental research, offering essential data on landforms, drainage patterns, and different environmental options. This data is essential for understanding and mitigating the influence of pure hazards corresponding to floods and landslides.
- Army Purposes: Topographical maps are important for army planning and operations, offering essential data on terrain, elevation, and obstacles. This data is essential for strategic planning, troop deployment, and logistical operations.
- Leisure Actions: Hikers, climbers, and different outside lovers depend on topographical maps for navigation and route planning. The map gives essential data on elevation, slope, and path places.
Conclusion:
A topographical map of North America is a strong visible software that gives invaluable insights into the continent’s bodily geography. By fastidiously decoding its contour traces, spot heights, and different options, we are able to acquire a deeper understanding of the geological processes which have formed the panorama, the affect of local weather on landforms, and the advanced interaction between human actions and the surroundings. From understanding the vastness of the plains to appreciating the grandeur of the mountain ranges, the map serves as a key to unlocking the secrets and techniques of this numerous and dynamic continent. Its purposes are huge and proceed to evolve as know-how advances, making it an indispensable useful resource for a variety of disciplines and endeavors.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Deciphering the Land: A Deep Dive into the Topographical Map of North America. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!