Farming the Future: A Deep Dive into the World of Farm Maps and Precision Agriculture
Associated Articles: Farming the Future: A Deep Dive into the World of Farm Maps and Precision Agriculture
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Farming the Future: A Deep Dive into the World of Farm Maps and Precision Agriculture. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Farming the Future: A Deep Dive into the World of Farm Maps and Precision Agriculture
The picture of a farmer tilling the land with a mule and plow is fading quick. Right now’s agriculture is more and more reliant on know-how, and on the coronary heart of this technological revolution lies the farm map. Not a easy visible illustration of land boundaries, farm maps have developed into subtle, data-rich instruments essential for optimizing yields, minimizing environmental affect, and maximizing profitability. This text explores the multifaceted world of farm maps, delving into their numerous sorts, functions, and the transformative affect they’re having on the worldwide meals system.
Past Boundaries: The Evolution of Farm Maps
Initially, farm maps served a primarily cadastral objective – defining property traces and possession. These have been usually easy hand-drawn sketches or rudimentary surveys. Nevertheless, the arrival of Geographic Data Techniques (GIS) and International Positioning Techniques (GPS) revolutionized the sector. Now, farm maps are dynamic, layered paperwork incorporating an unlimited quantity of knowledge past mere boundaries.
Sorts of Farm Maps and Their Purposes:
The varieties of farm maps utilized rely closely on the particular wants of the farm and the know-how accessible. Some frequent sorts embody:
-
Base Maps: These are the foundational layers, offering the geographical context. They usually embody options like roads, rivers, and subject boundaries derived from aerial imagery, satellite tv for pc information, and even drone surveys. Excessive-resolution imagery permits for exact delineation of options, essential for focused functions.
-
Soil Maps: These maps are important for precision agriculture. They depict the variation in soil kind, texture, pH, and nutrient content material throughout the farm. This info is essential for variable price fertilization and irrigation, making certain that inputs are optimized for every particular space, minimizing waste and maximizing nutrient uptake. Soil maps may be created by means of soil sampling, laboratory evaluation, and geostatistical modeling.
-
Topography Maps: These maps present the elevation variations throughout the farm. Understanding the topography is significant for environment friendly drainage administration, irrigation planning, and minimizing soil erosion. Contour traces or digital elevation fashions (DEMs) are generally used to characterize this information.
-
Yield Maps: Collected utilizing yield screens built-in into harvesting equipment, these maps show the crop yield for every space of the sector. Analyzing yield maps helps farmers determine areas of excessive and low productiveness, permitting them to research the underlying causes and implement corrective measures in subsequent rising seasons. Elements reminiscent of soil situations, pest infestations, and irrigation effectivity may be correlated with yield variations.
-
Prescription Maps: These maps are generated primarily based on information from different map layers, reminiscent of soil maps and yield maps. They supply particular suggestions for inputs like fertilizer, seeds, and pesticides for every space of the sector. This enables for focused utility, optimizing useful resource use and minimizing environmental affect. Precision utility applied sciences, reminiscent of variable price know-how (VRT), are used to implement the prescriptions.
-
Weed Maps: Generated by means of picture evaluation from drones or satellites, weed maps determine areas with excessive weed strain. This enables for focused herbicide utility, decreasing herbicide use and mitigating the event of herbicide resistance.
-
Illness and Pest Maps: Just like weed maps, these maps determine areas affected by illnesses or pests. This enables for well timed intervention, stopping widespread injury and minimizing the necessity for broad-spectrum remedies. Distant sensing strategies are sometimes used to detect early indicators of illness or pest infestations.
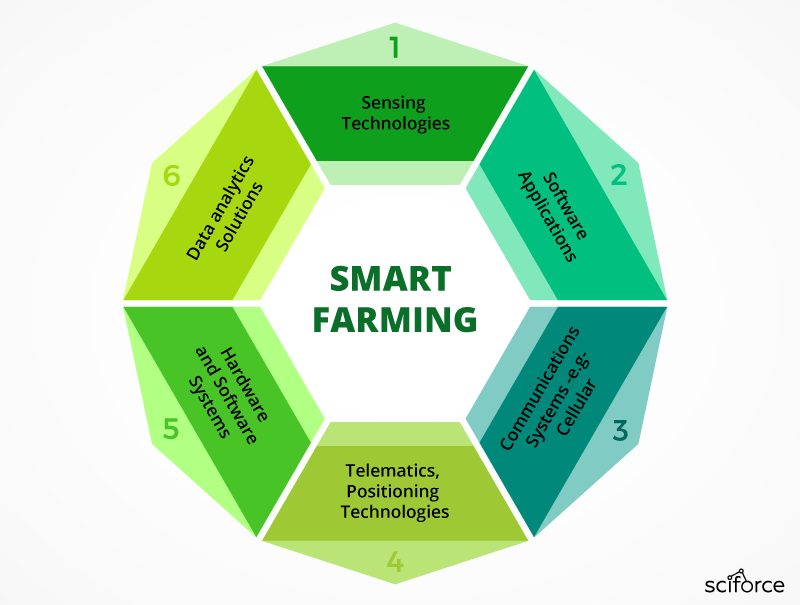
Applied sciences Driving Farm Mapping:
A number of applied sciences are instrumental in creating and using farm maps:
-
GPS (International Positioning System): Offers correct location information, important for georeferencing all information layers.
-
GIS (Geographic Data Techniques): A software program system for capturing, storing, analyzing, managing, and presenting all varieties of geographical information.
-
Distant Sensing: Using satellite tv for pc or drone imagery to gather information on crop well being, weed strain, and different elements.
-
Yield Displays: Built-in into harvesting equipment to gather real-time yield information.
-
Sensors and IoT (Web of Issues): Varied sensors can monitor soil moisture, temperature, and different environmental elements, offering real-time information for knowledgeable decision-making.
-
Machine Studying and AI: Used to research giant datasets from numerous sources to determine patterns, predict yields, and optimize useful resource allocation.
Advantages of Using Farm Maps:
The adoption of farm maps presents a wide selection of advantages:
-
Elevated Effectivity: Optimized useful resource allocation (fertilizer, water, pesticides) results in price financial savings and decreased environmental affect.
-
Improved Yields: Focused interventions primarily based on exact information result in larger crop yields and improved profitability.
-
Decreased Environmental Influence: Minimized use of inputs reduces air pollution and promotes sustainable agriculture.
-
Higher Resolution-Making: Information-driven insights allow farmers to make knowledgeable choices primarily based on real-time info.
-
Enhanced Farm Administration: Offers a complete overview of the farm’s assets and operations.
-
Improved Traceability: Detailed data of inputs and practices improve traceability and compliance with laws.
Challenges and Concerns:
Regardless of the quite a few advantages, there are challenges related to the widespread adoption of farm maps:
-
Price of Know-how: The preliminary funding in {hardware} and software program may be vital, significantly for smaller farms.
-
Information Administration: Managing giant datasets requires experience and acceptable infrastructure.
-
Information Accuracy: The accuracy of the information depends upon the standard of the enter information and the applied sciences used.
-
Connectivity: Dependable web connectivity is essential for accessing and using information in real-time.
-
Technical Experience: Farmers want enough coaching and assist to successfully make the most of the know-how.
The Way forward for Farm Maps:
The way forward for farm mapping is brilliant. Developments in know-how, such because the elevated use of synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML), will additional improve the capabilities of farm maps. We will count on to see:
-
Extra subtle predictive fashions: AI and ML will allow extra correct predictions of yields, illness outbreaks, and different elements affecting crop manufacturing.
-
Integration with different farm administration programs: Farm maps will probably be seamlessly built-in with different farm administration software program, offering a holistic view of farm operations.
-
Elevated use of drone know-how: Drones will present high-resolution imagery and information assortment at a decrease price than satellites.
-
Larger accessibility: Efforts to cut back the price and complexity of farm mapping applied sciences will make them extra accessible to smaller farms.
Conclusion:
Farm maps have developed from easy visible representations to highly effective instruments driving the transformation of agriculture. They’re important for attaining sustainable and environment friendly meals manufacturing within the face of rising world challenges. By embracing the potential of farm maps and associated applied sciences, farmers can enhance their productiveness, scale back their environmental footprint, and construct a extra resilient and sustainable meals system for the long run. The journey in direction of precision agriculture is ongoing, and farm maps will proceed to play a pivotal position in shaping the way forward for farming.



![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Farming the Future: A Deep Dive into the World of Farm Maps and Precision Agriculture. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!