Mapping the Bay Space’s Seismic Shake: Understanding Earthquake Danger By means of Geographic Info
Associated Articles: Mapping the Bay Space’s Seismic Shake: Understanding Earthquake Danger By means of Geographic Info
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Mapping the Bay Space’s Seismic Shake: Understanding Earthquake Danger By means of Geographic Info. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Bay Space’s Seismic Shake: Understanding Earthquake Danger By means of Geographic Info

The San Francisco Bay Space, a vibrant hub of innovation and tradition, sits precariously atop a fancy community of energetic faults. Understanding the area’s seismic vulnerability is paramount for mitigating threat and making certain neighborhood resilience. This text delves into the intricate relationship between geography and earthquake threat within the Bay Space, exploring how maps visualize this advanced interaction and inform essential decision-making processes.
Geological Setting: A Tectonic Tapestry
The Bay Space’s susceptibility to earthquakes stems immediately from its location on the boundary between two main tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The Pacific Plate is shifting northwestward relative to the North American Plate, a course of that generates immense stress alongside the fault strains crisscrossing the area. These faults, basically fractures within the Earth’s crust, act as conduits for the discharge of gathered power, leading to earthquakes of various magnitudes. Essentially the most distinguished amongst these is the San Andreas Fault, a remodel boundary stretching over 800 miles, slicing a major swathe by means of the Bay Space.
Nevertheless, the seismic panorama is not restricted to the San Andreas. Quite a few different important faults, together with the Hayward Fault, the Rodgers Creek Fault, and the Calaveras Fault, contribute to the world’s advanced seismic profile. These faults, typically exhibiting intricate branching patterns and ranging levels of exercise, create a mosaic of earthquake hazards throughout the Bay Space. Mapping these faults precisely is essential for understanding the spatial distribution of earthquake threat.
Earthquake Maps: Visualizing Danger
Earthquake maps function important instruments for visualizing and quantifying this threat. These maps make the most of a wide range of information sources, together with geological surveys, historic earthquake information, and complex geophysical modeling, to signify totally different features of seismic hazard. A number of key forms of earthquake maps are utilized:
-
Fault Maps: These maps depict the areas and geometries of recognized energetic faults. They’re essential for figuring out areas immediately adjoining to fault strains, which expertise the very best ranges of floor shaking throughout an earthquake. Excessive-resolution fault maps, incorporating latest geological surveys and geophysical information, are continually being up to date and refined to enhance accuracy.
-
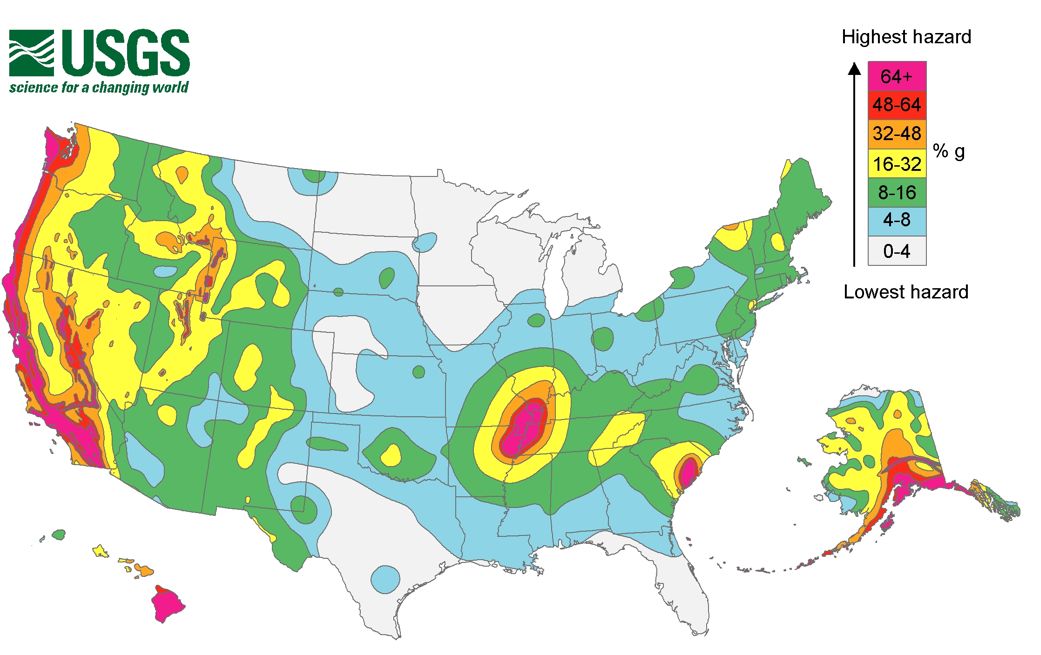
Shake Maps: These maps illustrate the anticipated depth of floor shaking following an earthquake. They’re typically generated in real-time following an earthquake occasion, utilizing seismic wave information from monitoring stations. Shake maps make the most of scales such because the Modified Mercalli Depth (MMI) scale, which describes the consequences of shaking on individuals, constructions, and the atmosphere. They’re important for emergency response and harm evaluation.
-
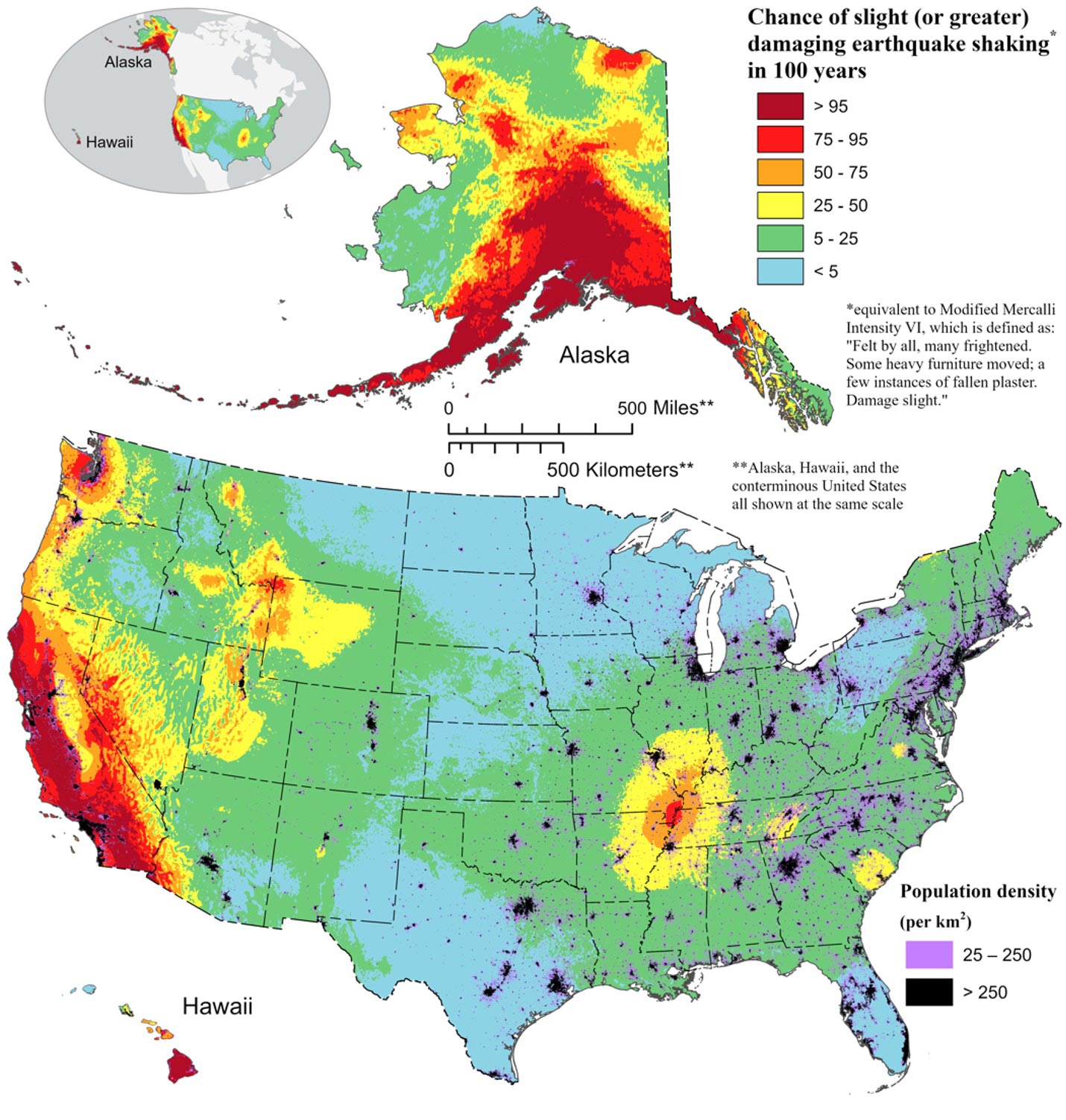
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps (PSHA): These maps signify the likelihood of exceeding a sure degree of floor shaking at a given location over a selected time interval (e.g., 50 years). They incorporate uncertainties in fault areas, earthquake recurrence intervals, and floor movement prediction equations, offering a extra complete evaluation of long-term seismic threat. PSHA maps are instrumental in constructing codes, infrastructure planning, and land-use choices.
-
Liquefaction Susceptibility Maps: These maps determine areas vulnerable to liquefaction, a phenomenon the place saturated soil loses its power and behaves like a liquid throughout an earthquake. Liquefaction may cause important harm to buildings and infrastructure, resulting in floor subsidence and basis failure. These maps are essential for guiding development practices and mitigating liquefaction-related dangers.
-
Tsunami Inundation Maps: Whereas much less immediately associated to floor shaking, these maps depict the potential extent of tsunami inundation in coastal areas following a serious earthquake. The Bay Space, significantly its shoreline, is weak to tsunamis generated by earthquakes alongside the Cascadia Subduction Zone or elsewhere within the Pacific Ocean.
Information Sources and Technological Developments
The creation of correct and complete earthquake maps depends on a mess of information sources and complex applied sciences. Geological surveys contain detailed discipline investigations, trenching, and geophysical strategies to map fault areas and traits. Seismic monitoring networks, consisting of densely spaced seismometers, present real-time information on earthquake occurrences and floor movement. Advances in Geographic Info Programs (GIS) and distant sensing applied sciences, resembling LiDAR (Mild Detection and Ranging), improve the precision and element of mapping efforts. Moreover, refined computational fashions and probabilistic strategies are employed to generate PSHA maps, incorporating uncertainties and offering a statistically strong evaluation of seismic hazard.
Utilizing Maps for Danger Mitigation and Neighborhood Resilience
Earthquake maps aren’t merely tutorial workouts; they’re essential instruments for mitigating threat and constructing neighborhood resilience. They inform:
-
Constructing Codes and Laws: Constructing codes are designed to make sure constructions can face up to the anticipated ranges of floor shaking in a selected location. PSHA maps and liquefaction susceptibility maps are important inputs for establishing applicable constructing requirements.
-
Infrastructure Planning and Design: Essential infrastructure, resembling hospitals, faculties, and transportation networks, must be designed and positioned to attenuate seismic vulnerability. Earthquake maps assist determine high-risk areas and information the event of resilient infrastructure.
-
Land-Use Planning and Growth: Land-use planning choices ought to contemplate seismic hazards to attenuate potential losses and shield communities. Earthquake maps can information zoning laws, growth restrictions, and the placement of emergency shelters.
-
Emergency Preparedness and Response: Shake maps and different real-time information are essential for emergency responders to evaluate harm, prioritize rescue efforts, and allocate sources successfully following an earthquake.
-
Public Schooling and Consciousness: Earthquake maps can be utilized to coach the general public about seismic hazards and promote preparedness. Understanding the dangers of their particular areas empowers people to take applicable actions to guard themselves and their households.
Challenges and Future Instructions
Regardless of important developments, challenges stay in mapping the Bay Space’s seismic panorama. The complexity of fault programs, uncertainties in earthquake recurrence intervals, and the restrictions of geophysical fashions contribute to uncertainties in threat assessments. Moreover, the continuing tectonic processes imply that fault areas and exercise ranges can evolve over time, necessitating steady monitoring and updates to earthquake maps. Future instructions embody incorporating superior geophysical strategies, enhancing floor movement prediction fashions, and creating extra refined probabilistic strategies to refine threat assessments. The combination of synthetic intelligence and machine studying strategies holds promise for automating information evaluation and enhancing the accuracy and effectivity of earthquake mapping.
In conclusion, earthquake maps are indispensable instruments for understanding and mitigating seismic threat within the San Francisco Bay Space. By visualizing the advanced interaction between geology, tectonics, and seismic hazard, these maps empower communities to make knowledgeable choices, construct resilient infrastructure, and improve preparedness for future earthquakes. Continued developments in mapping applied sciences and information evaluation might be vital for refining threat assessments and enhancing the security and well-being of the Bay Space’s inhabitants.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Mapping the Bay Space’s Seismic Shake: Understanding Earthquake Danger By means of Geographic Info. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!