Mapping the Large: A Deep Dive into China’s Inhabitants Distribution
Associated Articles: Mapping the Large: A Deep Dive into China’s Inhabitants Distribution
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Mapping the Large: A Deep Dive into China’s Inhabitants Distribution. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Large: A Deep Dive into China’s Inhabitants Distribution
China, the world’s most populous nation, presents a captivating case research in inhabitants geography. Its huge landmass, various topography, and sophisticated historical past have formed a inhabitants distribution that’s removed from uniform, revealing intricate patterns of density and sparsity. Understanding this distribution is essential for comprehending China’s financial improvement, social dynamics, and future challenges. This text will delve into the intricacies of China’s inhabitants map, analyzing its key options, historic influences, and implications for the nation’s ongoing transformation.
Historic Context: From Agrarian Roots to City Growth
For millennia, China’s inhabitants was predominantly rural and concentrated alongside fertile river valleys. The Yangtze and Yellow River basins, cradles of Chinese language civilization, witnessed the event of dense agricultural societies, supporting huge populations. These areas, notably the North China Plain, grew to become inhabitants hotspots, characterised by intensive farming and excessive inhabitants densities. Traditionally, entry to water sources, arable land, and transportation networks dictated settlement patterns. Coastal areas additionally noticed important populations, pushed by maritime commerce and fishing.
Nevertheless, the twentieth century caused seismic shifts. The communist revolution and subsequent collectivization of agriculture led to important rural-to-urban migration, albeit at a slower tempo initially. The implementation of the "hukou" system, a family registration system, restricted motion and strengthened rural-urban divides. Nonetheless, the post-Mao period witnessed a dramatic acceleration of urbanization, spurred by financial reforms and the rise of particular financial zones. This led to the emergence of megacities like Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, attracting tens of millions of migrants from rural areas searching for higher financial alternatives.
The Trendy Inhabitants Map: A Tapestry of Density and Dispersion
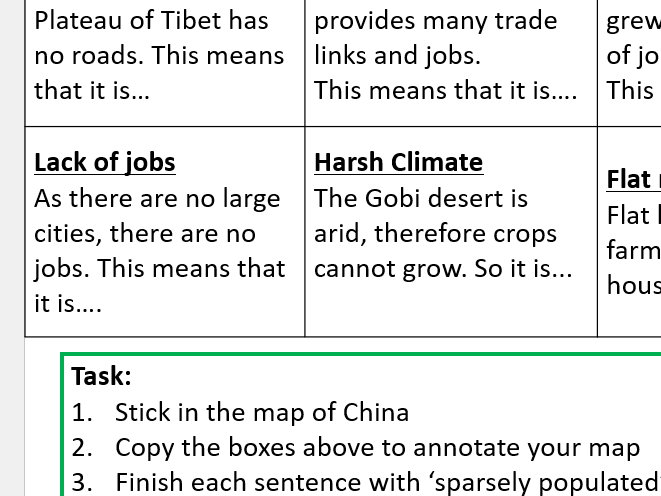
A contemporary inhabitants map of China reveals a posh tapestry of excessive and low density areas. Essentially the most hanging characteristic is the focus of inhabitants alongside the japanese seaboard. The coastal provinces of Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shandong boast exceptionally excessive inhabitants densities, fueled by industrialization, export-oriented manufacturing, and thriving service sectors. These areas are characterised by sprawling megacities, interconnected city agglomerations, and excessive ranges of infrastructure improvement.
In distinction, huge swathes of western China stay sparsely populated. The Tibetan Plateau, the Gobi Desert, and the mountainous areas of Xinjiang and Yunnan expertise considerably decrease inhabitants densities attributable to harsh environmental circumstances, restricted arable land, and difficult terrain. These areas typically characteristic nomadic or semi-nomadic populations, with settlement patterns dictated by entry to water and pastureland.
The inner migration patterns are clearly seen on the map. The strains of migration radiate outwards from the densely populated japanese coastal areas in the direction of the much less populated inside. This motion is pushed by financial disparities, with people searching for employment and higher residing requirements within the extra developed japanese provinces. Nevertheless, this migration additionally contributes to the rising challenges of city overcrowding, infrastructure pressure, and social inequality within the coastal cities.
Regional Variations and Their Implications:
Analyzing the inhabitants map on a regional foundation reveals additional nuances:
- North China Plain: Stays a densely populated area, however its development fee is slowing attributable to components like environmental degradation and water shortage.
- Yangtze River Delta: One of many world’s most dynamic financial areas, characterised by extraordinarily excessive inhabitants densities and speedy urbanization.
- Pearl River Delta: One other main financial powerhouse, experiencing comparable excessive inhabitants densities and speedy city enlargement.
- Northeast China: Experiencing inhabitants decline and deindustrialization, resulting in out-migration and a shrinking workforce.
- Western China: Governments are actively selling improvement on this area by means of initiatives just like the Belt and Highway Initiative, aiming to stimulate financial development and appeal to funding, however the challenges of infrastructure improvement and environmental sustainability stay important.
The One-Baby Coverage and its Legacy:
The implementation and subsequent rest of China’s one-child coverage (later two-child and now three-child insurance policies) have had a profound influence on the inhabitants distribution and demographics. Whereas initially aimed toward curbing inhabitants development, it led to an ageing inhabitants and a shrinking workforce, notably in rural areas. This demographic shift has implications for social safety programs, healthcare provision, and financial productiveness. The long-term results of those insurance policies are nonetheless unfolding and can proceed to form China’s inhabitants map for many years to return.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
China’s inhabitants map presents each alternatives and challenges. The focus of inhabitants within the east necessitates cautious city planning to handle points like overcrowding, air pollution, and useful resource administration. The comparatively low inhabitants density within the west presents alternatives for improvement, however overcoming infrastructural limitations and environmental constraints stays a major hurdle.
The ageing inhabitants poses a major problem, requiring reforms to pension programs, healthcare provision, and labor market insurance policies. Addressing the rural-urban divide, bettering entry to schooling and healthcare in much less developed areas, and selling sustainable improvement are essential for guaranteeing a balanced and equitable inhabitants distribution.
Conclusion:
China’s inhabitants map is a dynamic and sophisticated entity, reflecting centuries of historic improvement and the speedy transformations of the previous few a long time. Understanding its intricacies is important for policymakers, researchers, and anybody searching for to understand China’s financial, social, and environmental trajectory. The interaction between historic components, authorities insurance policies, and environmental constraints continues to form the distribution of China’s huge inhabitants, presenting each alternatives and challenges for the long run. Continued monitoring and evaluation of this dynamic map are essential for navigating the complexities of China’s demographic panorama and guaranteeing its sustainable improvement.



![[July.2024]A Deep Dive into McDonald's: decoding the earnings of the](https://uscourseimg.moomoo.com/1721975979028.jpeg?imageMogr2/quality/100/ignore-error/1)


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Mapping the Large: A Deep Dive into China’s Inhabitants Distribution. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!