Mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry
Associated Articles: Mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry

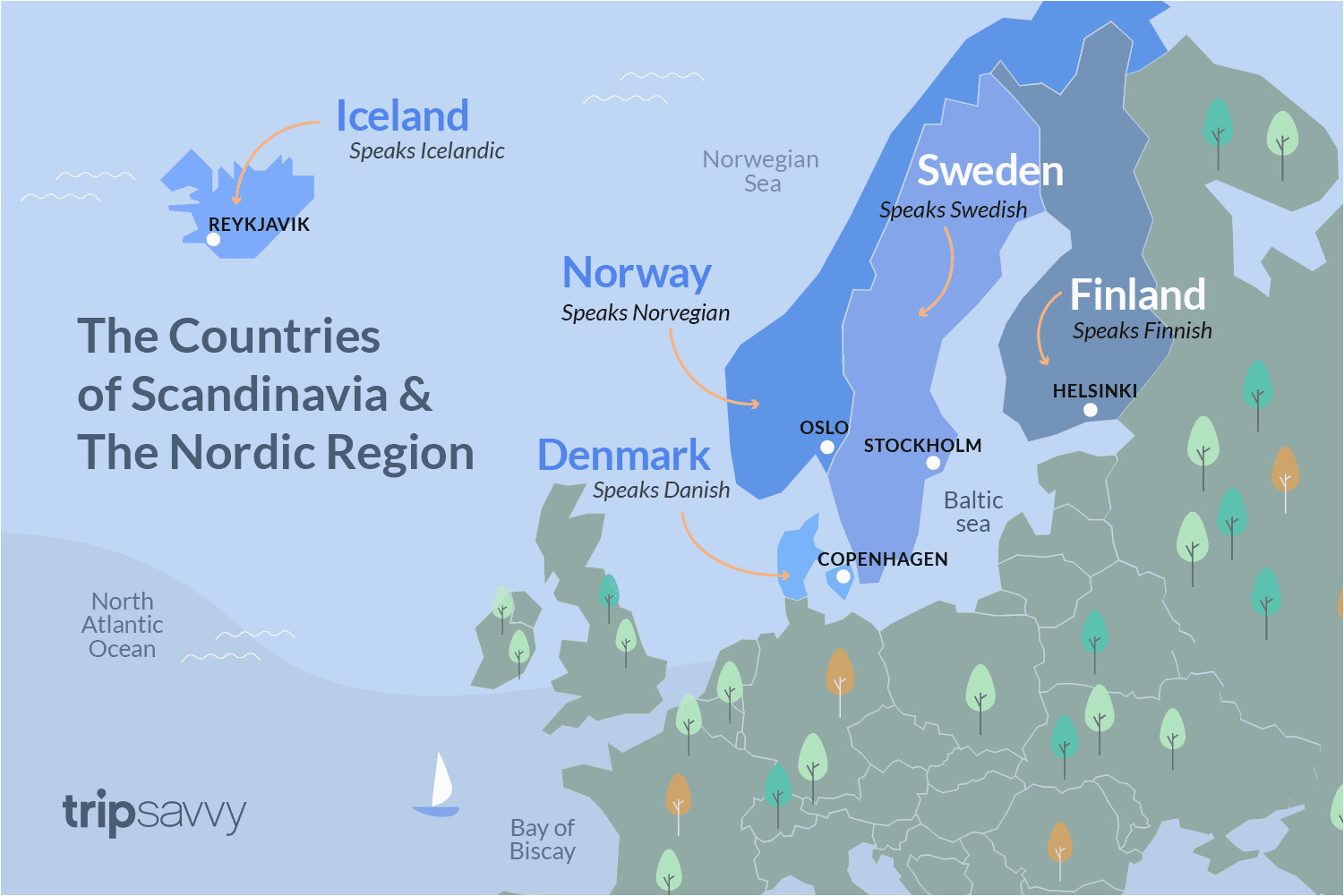
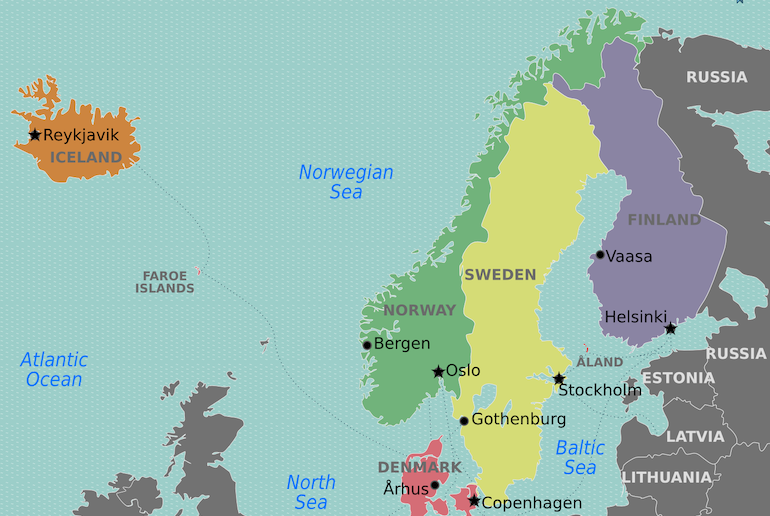
The Scandinavian Peninsula, a dramatic landmass jutting out from Northern Europe, is a area of breathtaking landscapes, wealthy historical past, and distinct cultural identities. Its distinctive geography, formed by millennia of glacial exercise and tectonic forces, has profoundly influenced the lives and societies of its inhabitants. Mapping this peninsula, subsequently, requires greater than merely plotting geographical coordinates; it necessitates understanding the advanced interaction of bodily options, human settlements, and historic occasions which have formed its character.
A Land Formed by Ice and Fireplace:
The peninsula’s bodily geography is dominated by the interaction of mountains, fjords, and huge plains. The Scandinavian Mountains, or Kjølen, kind a backbone working alongside the peninsula’s jap edge, separating Norway from Sweden. These historical mountains, sculpted by repeated glacial cycles, attain spectacular heights, with Galdhøpiggen in Norway claiming the title of the best peak. The proof of previous glaciation is ubiquitous: deep U-shaped valleys carved by glaciers, huge plains strewn with glacial erratics, and the attribute sculpted landscapes of the fjords.
The fjords, arguably probably the most iconic function of the Scandinavian panorama, are lengthy, slim inlets of the ocean that minimize deep into the land. Fashioned by glacial erosion, they create a shoreline of outstanding complexity and sweetness. Norway, particularly, is famend for its gorgeous fjord landscapes, with Sognefjord, the longest and deepest fjord, being a major instance. These fjords have performed a vital position within the historical past of the area, offering entry to the ocean for fishing and commerce, and shaping settlement patterns alongside their shores.
In distinction to the mountainous west and north, southern Sweden and components of Denmark are characterised by flatter terrain, together with intensive plains and fertile agricultural lands. These areas have traditionally been extra conducive to agriculture and denser inhabitants settlements, contrasting with the extra sparsely populated mountainous areas. The variations in topography have led to distinct regional variations in local weather, vegetation, and human exercise.
Mapping the Human Panorama:
Mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula requires contemplating not simply its bodily options but in addition the distribution of human settlements and infrastructure. The most important cities, corresponding to Oslo (Norway), Stockholm (Sweden), Copenhagen (Denmark), and Helsinki (Finland – though technically not on the peninsula itself, it is carefully linked geographically and culturally), are essential factors on any map. These city facilities aren’t solely inhabitants hubs but in addition financial and cultural drivers for his or her respective international locations.
The distribution of inhabitants is much from uniform. Coastal areas, significantly these with entry to fjords and sheltered bays, have traditionally been extra densely populated than the inside highlands. This sample is seen within the density of settlements alongside the Norwegian coast and within the southern areas of Sweden. The provision of assets, corresponding to fertile land and fishing grounds, has considerably influenced the placement of cities and villages all through historical past.
Fashionable infrastructure, together with roads, railways, and airports, performs a vital position in connecting the disparate components of the peninsula. The challenges posed by the rugged terrain have led to progressive engineering options, corresponding to intensive highway networks winding by means of mountainous areas and elaborate ferry methods connecting coastal communities. Mapping this infrastructure is crucial for understanding the connectivity and accessibility of various areas.
Historic and Cultural Layers:
The map of the Scandinavian Peninsula isn’t merely a static illustration of its present state; it additionally displays its wealthy and complicated historical past. The Viking Age, a interval of enlargement and exploration from roughly the eighth to the eleventh centuries, left an enduring imprint on the area and past. Viking settlements, commerce routes, and raiding expeditions are essential historic layers that may be overlaid onto a contemporary map for instance the extent of their affect.
The following growth of kingdoms and nation-states, the unfold of Christianity, and the emergence of distinct cultural identities are all interwoven into the material of the area’s historical past. Mapping these historic occasions requires a multi-layered method, integrating historic maps, archaeological findings, and textual proof to create a dynamic illustration of the peninsula’s previous.
The linguistic variety of the area is one other essential aspect to contemplate. Whereas Scandinavian languages share a standard ancestor, they’ve advanced into distinct varieties in Norway, Sweden, Denmark, and Iceland. Mapping the distribution of those languages reveals the advanced linguistic panorama of the area and highlights the cultural boundaries which have emerged over time.
Environmental Issues:
The Scandinavian Peninsula is more and more dealing with the impacts of local weather change. Rising sea ranges pose a risk to coastal communities and infrastructure, whereas adjustments in temperature and precipitation patterns are affecting agriculture, forestry, and the fragile ecosystems of the area. Mapping these environmental adjustments, together with glacial retreat, adjustments in vegetation patterns, and the rising frequency of maximum climate occasions, is essential for understanding the vulnerabilities of the peninsula and growing efficient adaptation methods.
Moreover, the administration of pure assets, corresponding to forests, fisheries, and mineral deposits, is a essential subject for the area’s sustainable growth. Mapping these assets and their distribution helps in planning for accountable useful resource administration and minimizing environmental impacts.
A Multi-Dimensional Map:
In conclusion, mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula is a fancy endeavor that goes past easy cartography. It requires a multi-dimensional method, integrating bodily geography, human settlements, historic occasions, cultural identities, and environmental issues. A complete map of the area shouldn’t solely present the placement of mountains, rivers, and cities but in addition convey the wealthy tapestry of human exercise, historic transformations, and environmental challenges which have formed this outstanding nook of the world. Such a map could be a testomony to the intricate relationship between humanity and the atmosphere, reflecting the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the Scandinavian Peninsula. It could be a software not only for navigation, however for understanding, appreciating, and defending this distinctive and charming area.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Mapping the Scandinavian Peninsula: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!