Mapping the World: From Cave Work to Digital Globes
Associated Articles: Mapping the World: From Cave Work to Digital Globes
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Mapping the World: From Cave Work to Digital Globes. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the World: From Cave Work to Digital Globes

Maps. They’re ubiquitous, woven into the material of our each day lives. From the paper maps tucked into glove compartments to the digital globes on our smartphones, maps information us, inform us, and join us to the world. However maps are excess of easy navigational instruments; they’re highly effective devices of communication, storytelling, and even political energy. This text delves into the wealthy historical past, numerous kinds, and evolving applied sciences of mapmaking, exploring its enduring significance in our understanding and shaping of the world.
A Historical past Painted on Partitions and Papyrus:
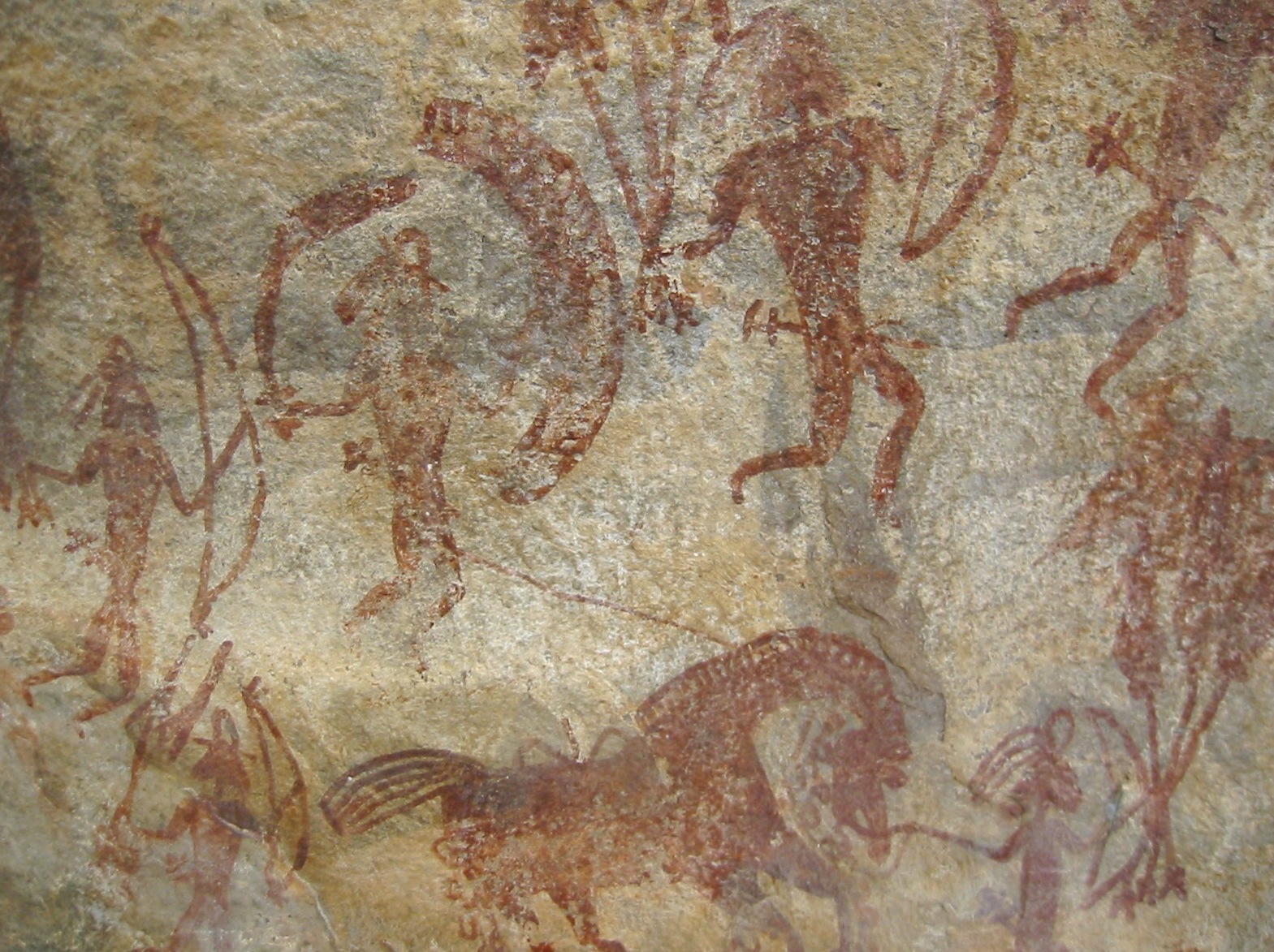
The earliest types of mapping weren’t the exact, scaled representations we’re accustomed to. As an alternative, they have been rudimentary sketches etched onto cave partitions, depicting territories, searching grounds, and important landmarks. These proto-maps, present in varied elements of the world, reveal a elementary human want to grasp and characterize spatial relationships. The Babylonian clay tablets, relationship again to the seventh century BC, present a few of the earliest examples of extra formalized cartography. These tablets depict the identified world, displaying rivers, mountains, and cities, albeit with a substantial diploma of symbolic illustration slightly than exact measurement.
The Greeks, with their emphasis on motive and remark, considerably superior the science of cartography. Anaximander, within the sixth century BC, is credited with creating one of many first world maps, a flat illustration depicting the Earth as a disc surrounded by water. Later, Ptolemy’s "Geographia" (2nd century AD) grew to become a cornerstone of cartography for hundreds of years, establishing a system of latitude and longitude that influenced mapmaking for over a millennium. Whereas Ptolemy’s map contained inaccuracies, its systematic strategy and the detailed descriptions of locations it contained revolutionized the sector.
The Center Ages noticed a shift in cartographic focus. Medieval maps, typically often called mappae mundi, have been much less involved with exact geographical accuracy and extra centered on representing the world in response to theological and philosophical viewpoints. Jerusalem was usually positioned on the heart, reflecting its spiritual significance, and the maps typically included symbolic components and illustrations of biblical occasions. These maps, although visually putting and traditionally invaluable, differed considerably from the extra scientific approaches of the classical world.
The Age of Exploration and Scientific Revolution:
The Age of Exploration, starting within the fifteenth century, spurred a renewed curiosity in correct cartography. Navigators wanted exact maps to chart new sea routes and discover uncharted territories. The invention of the printing press facilitated the mass manufacturing and dissemination of maps, resulting in better standardization and enhancements in accuracy. Cartographers like Gerardus Mercator developed new map projections, such because the Mercator projection, which, whereas distorting the sizes and styles of landmasses at increased latitudes, proved invaluable for navigation.
The Scientific Revolution additional fueled developments in mapmaking. Improved surveying strategies, astronomical observations, and the event of recent mathematical instruments allowed for extra exact measurements and the creation of extra correct maps. The institution of nationwide surveying companies in varied international locations led to the systematic mapping of huge territories, contributing to the creation of detailed nationwide atlases.
From Paper to Pixels: The Digital Revolution in Mapping:
The twentieth and twenty first centuries have witnessed a dramatic transformation in cartography with the appearance of digital applied sciences. The event of Geographic Info Techniques (GIS) has revolutionized the way in which maps are created, analyzed, and used. GIS permits for the mixing of varied knowledge layers, similar to elevation, inhabitants density, land use, and infrastructure, creating extremely detailed and interactive maps. Distant sensing applied sciences, similar to satellite tv for pc imagery and aerial images, present huge quantities of information for map creation, permitting for the mapping of even probably the most distant areas of the world.
The rise of the web and cellular units has made maps readily accessible to billions of individuals. On-line mapping companies, similar to Google Maps and Bing Maps, present real-time navigation, road views, and a wealth of geographical data. These companies have essentially modified the way in which we work together with the environment, enabling simpler journey, environment friendly logistics, and improved emergency response. Moreover, the event of open-source mapping tasks, like OpenStreetMap, permits for collaborative mapmaking, empowering communities to contribute to the creation and upkeep of detailed and correct maps.
Past Navigation: The Numerous Functions of Maps:
The functions of maps prolong far past easy navigation. Maps are essential instruments in varied fields, together with:
- City Planning: Maps are used to investigate city progress patterns, plan infrastructure growth, and handle assets.
- Environmental Administration: Maps assist observe deforestation, monitor air pollution ranges, and handle pure assets.
- Public Well being: Maps are used to trace illness outbreaks, establish well being disparities, and plan public well being interventions.
- Catastrophe Response: Maps are important for coordinating emergency response efforts throughout pure disasters and different crises.
- Enterprise and Advertising: Maps assist companies analyze market demographics, optimize logistics, and goal advertising and marketing campaigns.
- Historic Analysis: Maps present invaluable insights into previous societies, their territories, and their interactions.
- Political Science: Maps are used to investigate political boundaries, voting patterns, and the distribution of energy.
The Moral Issues of Mapping:
Whereas maps supply highly effective instruments for understanding and shaping the world, it’s essential to acknowledge the moral concerns concerned of their creation and use. Maps may be biased, reflecting the views and priorities of their creators. The selection of map projection, for instance, can considerably affect the notion of dimension and distance. Moreover, the information used to create maps may be incomplete, inaccurate, or intentionally manipulated. It’s important to critically consider the sources and methodologies utilized in map creation and to concentrate on the potential biases embedded inside maps.
The rising use of location knowledge raises privateness issues. The gathering and use of private location knowledge by mapping companies and different organizations require cautious consideration of moral implications and the necessity for transparency and consumer consent.
The Way forward for Mapping:
The way forward for mapping is prone to be formed by continued developments in expertise. The combination of synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML) will allow the automation of map creation and evaluation, resulting in extra environment friendly and correct maps. The usage of 3D modelling and digital actuality (VR) will create immersive and interactive mapping experiences. Moreover, the event of recent sensor applied sciences, similar to LiDAR and hyperspectral imaging, will present much more detailed and nuanced knowledge for map creation.
The continuing growth of open-source mapping initiatives will proceed to democratize entry to mapping applied sciences and empower communities to contribute to the creation of extra correct and complete maps. As our understanding of the world continues to evolve, so too will the function of maps in shaping our understanding and interplay with the planet. From the earliest cave work to the delicate digital globes of at this time, maps stay a testomony to human ingenuity and our enduring quest to grasp and navigate our world. The way forward for mapping guarantees much more progressive instruments and functions, additional enriching our understanding and interplay with the advanced tapestry of the Earth.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Mapping the World: From Cave Work to Digital Globes. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!