Mastering JavaScript’s map() Technique: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Mastering JavaScript’s map() Technique: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Mastering JavaScript’s map() Technique: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering JavaScript’s map() Technique: A Complete Information
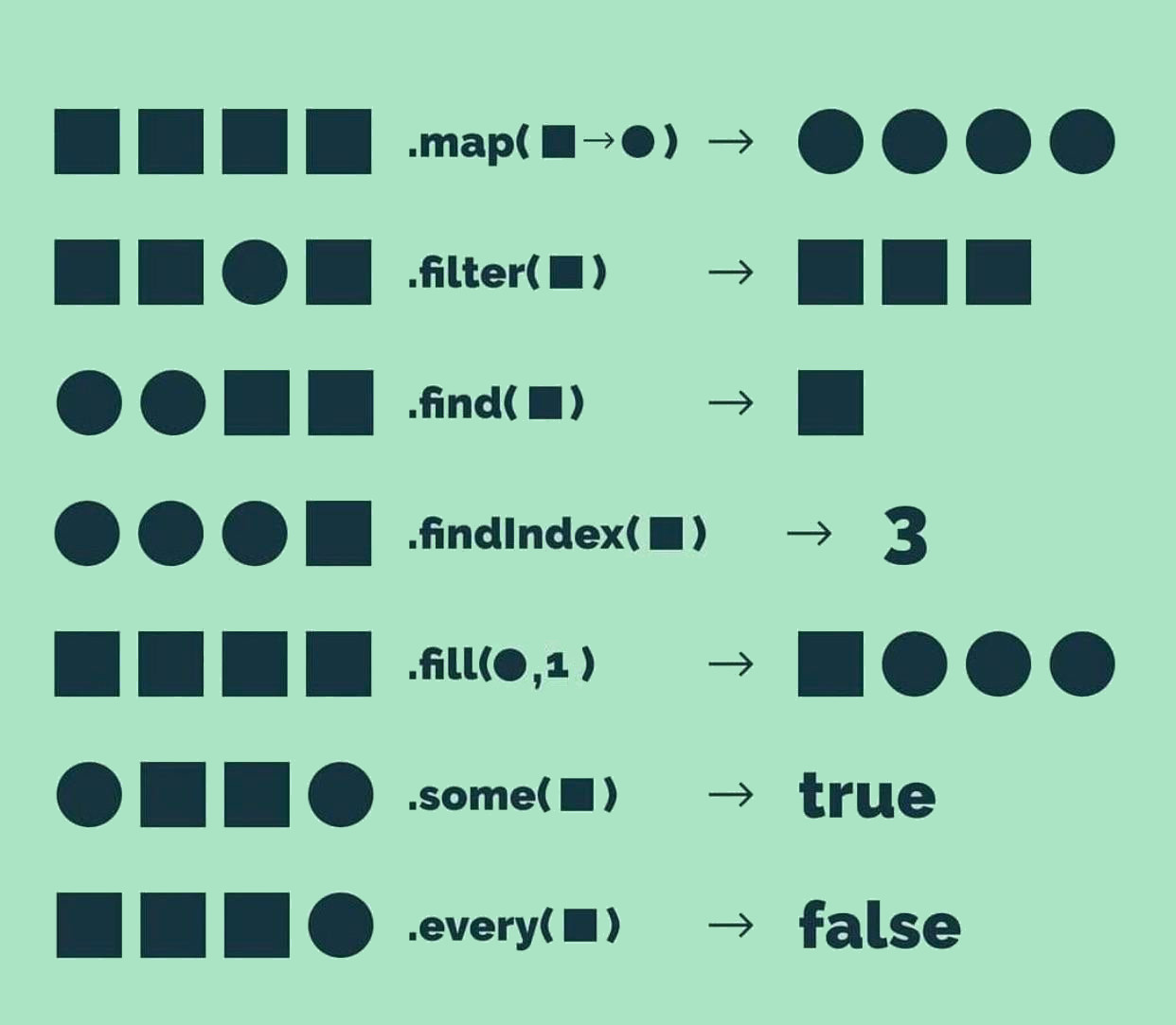
The map() methodology is a strong and versatile software in JavaScript’s arsenal, offering a concise and environment friendly solution to remodel arrays. It means that you can iterate over every component of an array, apply a perform to it, and create a brand new array containing the outcomes. This course of is key to purposeful programming paradigms and considerably simplifies many frequent array manipulation duties. Understanding map() is essential for writing clear, environment friendly, and readable JavaScript code.
This text dives deep into the map() methodology, exploring its core performance, utilization patterns, frequent pitfalls, and superior functions. We’ll cowl every part from fundamental examples to complicated eventualities, guaranteeing you acquire a complete understanding of this important JavaScript method.
Understanding the Core Performance
The map() methodology takes a callback perform as its argument. This callback perform is executed as soon as for every component within the array. The callback perform receives three arguments:
-
currentValue: The present component being processed within the array. -
index(optionally available): The index of the present component within the array. -
array(optionally available): The arraymap()is being known as upon.
The callback perform ought to return a worth for every component. These returned values are then used to assemble a brand new array, which is the results of the map() operation. Importantly, the unique array stays unchanged; map() creates a totally new array.
Fundamental Syntax and Instance
The fundamental syntax of the map() methodology is:
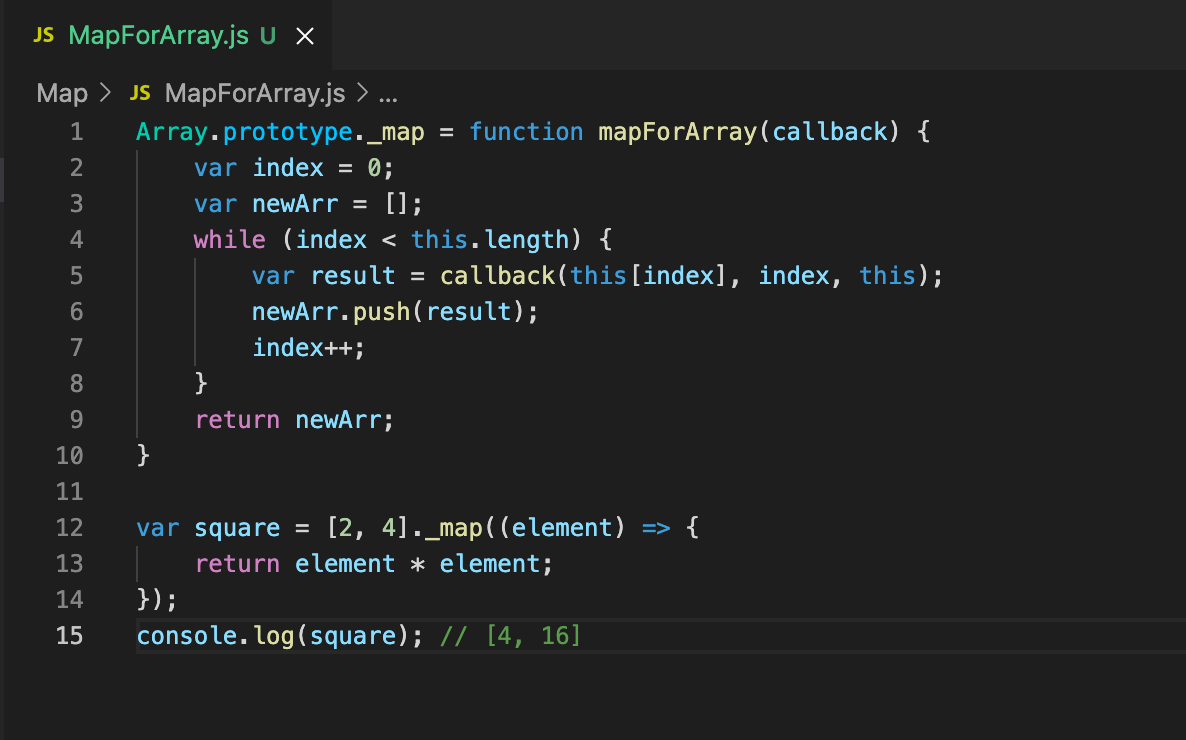
const newArray = array.map(callbackFn);Let’s think about a easy instance: Suppose we have now an array of numbers and wish to double every quantity.
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const doubledNumbers = numbers.map(quantity => quantity * 2);
console.log(doubledNumbers); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
console.log(numbers); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] (unique array unchanged)On this instance, the callback perform quantity => quantity * 2 is a concise arrow perform that merely multiplies every quantity by 2. The map() methodology applies this perform to every component within the numbers array, creating a brand new array doubledNumbers containing the doubled values. Discover that the unique numbers array stays untouched.
Utilizing the Index and Array Arguments
The callback perform also can make the most of the optionally available index and array arguments. For example, we would wish to create a brand new array the place every component is a string representing the quantity and its index:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const numberedStrings = numbers.map((quantity, index, array) => `$index: $quantity (from array: $array)`);
console.log(numberedStrings);
// Output: ['0: 1 (from array: 1,2,3,4,5)', '1: 2 (from array: 1,2,3,4,5)', '2: 3 (from array: 1,2,3,4,5)', '3: 4 (from array: 1,2,3,4,5)', '4: 5 (from array: 1,2,3,4,5)']Right here, the callback perform makes use of each the index and array arguments to assemble the string illustration of every component.
Working with Objects
The map() methodology is equally efficient when working with arrays of objects. For instance we have now an array of person objects, and we wish to extract solely their usernames:
const customers = [
id: 1, username: 'johnDoe' ,
id: 2, username: 'janeSmith' ,
id: 3, username: 'peterJones'
];
const usernames = customers.map(person => person.username);
console.log(usernames); // Output: ['johnDoe', 'janeSmith', 'peterJones']This instance demonstrates how map() can elegantly extract particular properties from an array of objects, creating a brand new array containing solely the specified knowledge.
Dealing with Empty Arrays
The map() methodology gracefully handles empty arrays. If the enter array is empty, it is going to return a brand new empty array with none errors:
const emptyArray = [];
const mappedEmptyArray = emptyArray.map(x => x * 2);
console.log(mappedEmptyArray); // Output: []Superior Purposes and Use Circumstances
Past fundamental transformations, map() can be utilized in additional complicated eventualities:
-
Information Cleansing and Preprocessing:
map()is invaluable for cleansing and preprocessing knowledge earlier than additional processing. For instance, you should use it to transform strings to numbers, trim whitespace, or deal with lacking values. -
Information Transformation for Rendering: In internet growth,
map()is incessantly used to rework knowledge right into a format appropriate for rendering within the person interface. For instance, you would possibly use it to rework an array of knowledge objects into an array of JSX components for React parts. -
Creating New Information Constructions:
map()can be utilized to create totally new knowledge buildings from current ones. For example, you could possibly remodel an array of numbers right into a nested array, a map, or a set. -
Chaining with Different Array Strategies: The facility of
map()is amplified when mixed with different array strategies likefilter(),scale back(), andkind(). This permits for complicated knowledge manipulation pipelines. For instance, you would possibly filter an array, then map the filtered outcomes, and eventually scale back the mapped outcomes to a single worth.
Frequent Pitfalls and Greatest Practices
Whereas map() is a strong software, there are some frequent pitfalls to keep away from:
-
Modifying the Authentic Array: Do not forget that
map()creates a new array. Making an attempt to switch the unique array throughout the callback perform won’t have an effect on the results of themap()operation. -
Facet Results: Maintain your callback capabilities pure. Keep away from negative effects like modifying international variables or making exterior API calls throughout the callback perform. This ensures predictability and maintainability.
-
Incorrect Callback Operate: Guarantee your callback perform appropriately processes every component and returns the anticipated worth. Errors within the callback perform can result in sudden outcomes or errors.
-
Overuse: Whereas
map()is flexible, it is not at all times the very best resolution. For easy operations, aforloop could be extra environment friendly. Select the best software for the job.
Alternate options to map()
Whereas map() is usually essentially the most elegant resolution for remodeling arrays, different strategies could be extra applicable in particular conditions:
-
forEach(): When you solely must iterate over an array and carry out negative effects (like modifying the DOM),forEach()is an appropriate various. Nonetheless,forEach()doesn’t return a brand new array. -
forloop: For easy transformations or when efficiency is crucial, a conventionalforloop could be extra environment friendly thanmap(). -
scale back(): If it is advisable to accumulate a single worth from the array (e.g., sum, common),scale back()is a extra applicable selection.
Conclusion
The JavaScript map() methodology is a basic software for any developer working with arrays. Its potential to rework arrays in a concise and environment friendly method makes it important for constructing sturdy and maintainable functions. By understanding its core performance, frequent use instances, and potential pitfalls, you possibly can leverage the complete energy of map() to put in writing cleaner, extra environment friendly, and extra expressive JavaScript code. Mastering map() is a big step in direction of turning into a proficient JavaScript programmer. Bear in mind to apply and experiment with totally different eventualities to solidify your understanding and construct confidence in utilizing this highly effective methodology. By combining map() with different array strategies, you will unlock even larger prospects for knowledge manipulation and transformation in your JavaScript tasks.



![[JavaScript] Mastering ES6 Class Syntax - Comprehensive Learning of](https://img.clonecoding.com/thumb/90/16x9/javascript-mastering-es6-class-syntax-comprehensive-learning-of-class-declaration-initialization-method-definition-and-inheritance.webp)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Mastering JavaScript’s map() Technique: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!
